High-content Screening Research Areas

High-content analysis (HCA) has expanded into all corners of life science since its beginnings in drug discovery and is now used widely in a diverse range of scientific research areas including oncology, neuroscience, infectious disease, and toxicology, to name just a few.
HCA merges the benefits of high-throughput automation and unbiased analysis with microscopic imaging. The combination of high sample throughput with multiparametric imaging and multivariate analysis enables the detection of even subtle phenotypic changes which isn’t possible with traditional laboratory techniques.
Discover how high-content analysis and screening can advance your research in a selection of areas.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
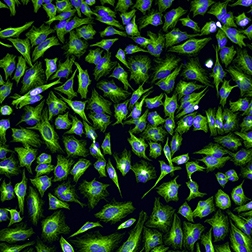
Cancer research
Cellular imaging has revolutionized cancer biology by enabling cells to be seen more clearly and in more detail as well as creating meaningful functional assays for the development of drugs which prevent tumor growth and metastasis.
Cellular imaging has revolutionized cancer biology by enabling cells to be seen more clearly and in more detail as well as creating meaningful functional assays for the development of drugs which prevent tumor growth and metastasis.
Cancer is a class of diseases in which a group of cells display new properties, such as hyperactive growth and division, protection against programmed cell death, loss of respect for normal tissue boundaries, and the ability to become established in diverse tissue environments.
Cancer research is an intense scientific effort to understand and discover disease processes and discover possible therapies. Advanced cellular imaging techniques allow us to visualize important aspects of cancer including tumor cell mobility, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis.
Scientists can distinguish host cells from a tumor with single-cell resolution. Visualization of many aspects of cancer initiation and progression in vivo is now possible, providing greater context and more accuracy to cancer research.
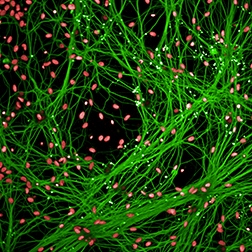
Neuroscience
High content analysis is a powerful tool for neuroscience that provides rich data for research including assays that can quantify various aspects of dendritic trees, protein aggregation, transcription factor translocation, neurotransmitter receptor internalization, neuron and synapse number, cell migration, proliferation and apoptosis.
High content analysis is a powerful tool for neuroscience that provides rich data for research including assays that can quantify various aspects of dendritic trees, protein aggregation, transcription factor translocation, neurotransmitter receptor internalization, neuron and synapse number, cell migration, proliferation and apoptosis.
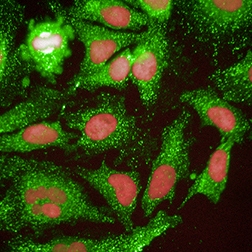
Infectious diseases
HCS plays a significant role in infectious disease research as it enables high throughput functional and phenotypic assays that can be adapted to a wide range of pathogens including virus, bacteria and eukaryotic parasites.
HCS plays a significant role in infectious disease research as it enables high throughput functional and phenotypic assays that can be adapted to a wide range of pathogens including virus, bacteria and eukaryotic parasites.
Applications include genetic siRNA interference screens for identifying host factors involved in host–pathogen interactions, but also screens for lead discovery in drug discovery. High-content analysis enables, for example, intracellular tracking of viral particles to profile the antiviral mechanisms of each compound and sensitive measurements of bacterial infection rates. Adaptation to high-throughput screening in bacteriology and parasitology has already led to the discovery of new types of host-specific inhibitors that differ from those inhibitors that act directly on microbes.
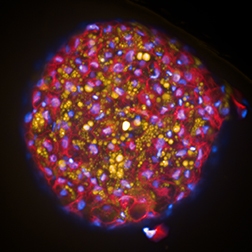
Toxicity
Undesired toxic side effects are still amongst the most common reasons for failure of new chemical entities during late stage drug development and can even lead to costly withdrawals of approved drugs from the market.
Undesired toxic side effects are still amongst the most common reasons for failure of new chemical entities during late stage drug development and can even lead to costly withdrawals of approved drugs from the market.
It is therefore necessary to assess compounds in the early phases of the discovery process reliably for potential geno-, hepato-, nephro and cardiotoxic liabilities in order to reduce development costs and increase research efficiency. High content screening is a cost effective tool to run dedicated toxicity tests on relevant model systems.
Such dedicated assays include micronuclei assays to identify genotoxic effects, cell health studies on heptatocytes and kidney cells, advanced assays on liver microtissues, or using primary human cells, hypertrophy studies on cardiomyocytes.
But even functional drug discovery HCS assays can provide important information on potential unwanted properties of a compound in addition to the primary effect readout.
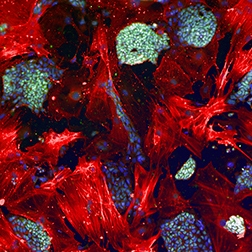
Stem cell research
High-content analysis is a powerful technology to analyze stem cell differentiation efficiently under a large variety of conditions and over long periods of times. Scientists are able visualize and analyze complex cellular processes, identify and characterize cells in their various stages of development.
High-content analysis is a powerful technology to analyze stem cell differentiation efficiently under a large variety of conditions and over long periods of times. Scientists are able visualize and analyze complex cellular processes, identify and characterize cells in their various stages of development.
Stem cell research has the potential to make a huge impact on a wide range of human health problems. Stem cell research could facilitate the development of new treatments for human diseases such as diabetes and Parkinson’s, aid the treatment and prevention of medical conditions resulting from abnormal cell division and cell differentiation, and enable the testing of new drugs without the need for animals or human testers. It could also provide a renewable source of replacement cells and tissues to treat diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, heart disease, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
For this fast paced area of research, Revvity provides state-of-the-art high content screening solutions to stem cell researchers all over the world. Our dedicated team of HCS specialists have an in-depth understanding of the imaging-based stem cell applications and will help you choose the right solution for your research requirements.


Filters
1 - 4 of 4 Products and Services
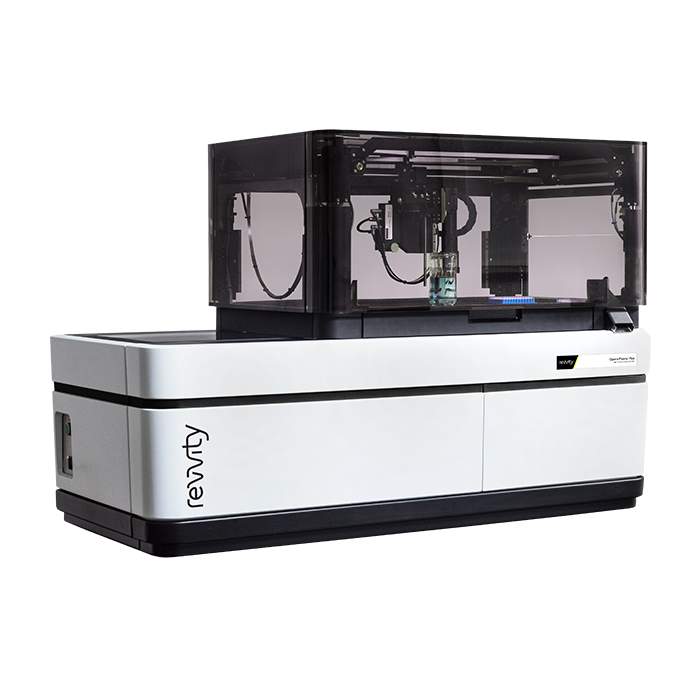
The Opera Phenix™ Plus high-content imaging system is a premier confocal solution for today’s most demanding high content applications. Drawing on over two decades of experience, the Opera Phenix Plus is designed for high-throughput high-content imaging assays, phenotypic screening, assays using complex disease models, such as live cells, primary cells and microtissues, and fast-response assays, such as Ca2+ flux.
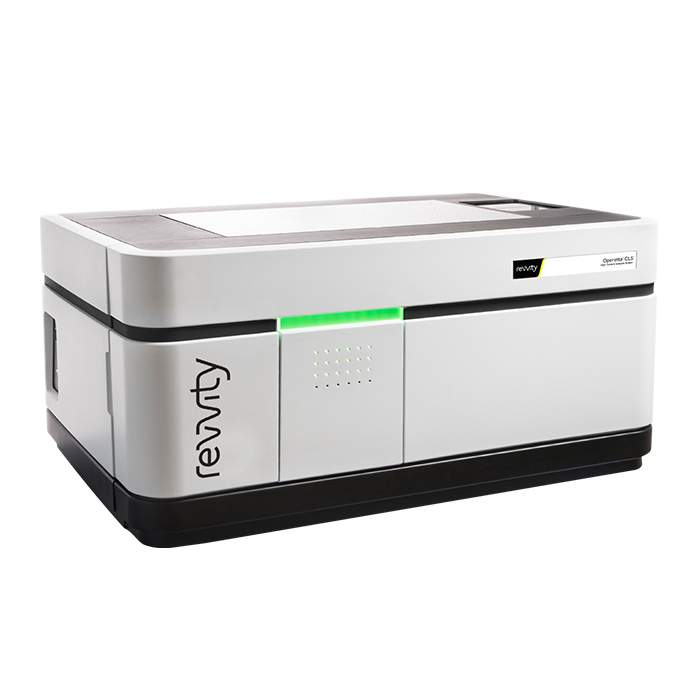
Uncover deep biological understanding in your everyday assays and innovative applications using the Operetta CLS™ high-content analysis system. Featuring a unique combination of technologies, the system delivers all the speed, sensitivity and resolution you need to reveal fine sub-cellular details. And with our simple, powerful Harmony software, Operetta CLS™ lets you find even subtle phenotypic changes.
PhenoLOGIC™ enables biologists using Harmony to train the software to develop the image analysis algorithms. While other systems may require an image analysis expert to create an algorithm, PhenoLOGIC uses proprietary machine-learning technology to make it easy for you to do it on your own. Using a learn-by-example approach, images can be segmented with just a few clicks of the mouse and then tailored algorithms developed quickly and easily.
Harness the power of intelligent image acquisition with PreciScan for more efficient high-content imaging and analysis. This optional plug-in for Harmony high-content analysis software enables you to more accurately target your object of interest for significantly reduced acquisition and analysis times, particularly valuable for 3D microtissue and rare event studies.